一、Channel介绍
Channel中的NioServerSocketChannel 和 NioSocketChannel 分别于 NIO中的 ServerSocketChannel、SocketChannel对应。不同的是,Netty的Channel将NIO中的Channel聚合在自己对象内部,并提供其他的功能操作。
二、Channel源码介绍
1. 常用方法介绍
| eventLoop() | Channel需要注册到EventLoop上的多路复用器上,通过该方法可获取到Channel注册的EventLoop(EventLoop本质就是处理网络读写事件的Reactor线程) |
| metadata() | 获取当前Channel的TCP参数配置 |
| parent() | 对于服务端而言,它的parent为空;对于客户端而言,它的父Channel就是创建它的ServerSocketChannel |
| id() | 获取Channel唯一标识对象 |
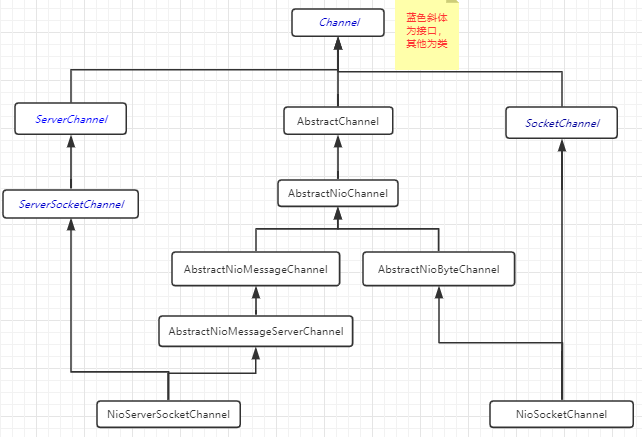
2. NioServerSocketChannel 和 NioSocketChannel 继承关系图
3. AbstractChannel源码分析
3.1 成员变量
private final Channel parent;//父类channel private final ChannelId id; //Channel唯一标识 private final Unsafe unsafe; private final DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline; // 当前Channel对应的默认的pipeline private final VoidChannelPromise unsafeVoidPromise = new VoidChannelPromise(this, false); private final CloseFuture closeFuture = new CloseFuture(this); private volatile SocketAddress localAddress; private volatile SocketAddress remoteAddress; private volatile EventLoop eventLoop; //当前Channel绑定的EventLoop private volatile boolean registered; //是否注册成功,在channelRegister(..)中被使用 private boolean closeInitiated; private Throwable initialCloseCause; /** Cache for the string representation of this channel */ private boolean strValActive; private String strVal;
3.2 网络读写操作
Netty基于事件驱动,当Channel进行IO操作时会产生对应的IO事件,然后驱动事件在ChannelPipeline中传播,由对应的ChannelHandler对事件进行拦截处理。
@Override public ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress) { return pipeline.connect(remoteAddress); } @Override public ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress) { return pipeline.connect(remoteAddress, localAddress); } @Override public ChannelFuture disconnect() { return pipeline.disconnect(); } ... 4. AbstractNioChannel源码分析
4.1 成员变量
//由于NioServerSocketChannel和NioSocketChannel都继承了该类,所以让这里持有ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel的父类,用于操作不同的Channel private final SelectableChannel ch; protected final int readInterestOp;//对应SeclectionKey.OP_READ //Channel注册到EventLoop后返回的选择键,Channel会面临多线程操作,可能修改了SelectionKey,volitile保证其可见性 volatile SelectionKey selectionKey; /** * The future of the current connection attempt. If not null, subsequent * connection attempts will fail. */ private ChannelPromise connectPromise;//连接操作结果 private ScheduledFuture connectTimeoutFuture;//连接超时定时器 private SocketAddress requestedRemoteAddress;//请求通信地址信息
4.2 Channel注册
protected void doRegister() throws Exception { boolean selected = false;//是否操作成功 for (;;) { try { // 调用SelectableChannel的register,将当前Channel注册到EventLoop的多路复用器上 // 这里注册的是0,表示不对任何事件感兴趣,只做注册操作 selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this); return; } catch (CancelledKeyException e) { // 如果当前注册返回的SelectionKey已经被取消,则抛出CancelledKeyException if (!selected) { // 如果是第一次处理该异常,则将已经取消的SelectionKey从多路复用器上删除 eventLoop().selectNow(); selected = true; } else { // 第二次注册失败,而且没有取消的SelectionKey可以删除,不应该出现 throw e; } } }} 5. AbstractNioByteChannel源码分析
5.1 成员变量
// 负责继续写半包消息 private final Runnable flushTask = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { ((AbstractNioUnsafe) unsafe()).flush0(); } }; 5.2 doWrite(...)
循环写,如果写完了则更新操作位后返回;如果指定循环次数没写完,或缓冲区写满了,则说明此次写了半包,注册写操作,继续写。
protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception { // 获取循环发送次数,默认16次 int writeSpinCount = config().getWriteSpinCount(); do { // 从消息环形数组中弹出一条消息 Object msg = in.current(); if (msg == null) { // 如果消息为空,说明所有消息发送数组中数据已发送完毕,清除半包标识,直接结束 clearOpWrite(); return; } // 还有待发送消息,继续处理并返回处理有效数(发送成功返回1,发送失败返回0) writeSpinCount -= doWriteInternal(in, msg); } while (writeSpinCount > 0); // 写完后的操作,走到这里,说明in.current()依然还有值,还有数据没有发送完毕 incompleteWrite(writeSpinCount < 0);}// 清除写操作位protected final void clearOpWrite() { final SelectionKey key = selectionKey(); if (!key.isValid()) { return; } final int interestOps = key.interestOps(); if ((interestOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) { //说明是isWritable,需要清除写操作 key.interestOps(interestOps & ~SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); }}private int doWriteInternal(ChannelOutboundBuffer in, Object msg) throws Exception { if (msg instanceof ByteBuf) { ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg; if (!buf.isReadable()) { in.remove(); return 0; } //进行消息发送,并返回发送了多少字节 final int localFlushedAmount = doWriteBytes(buf); if (localFlushedAmount > 0) { // 更新发送进度 in.progress(localFlushedAmount); if (!buf.isReadable()) { //判断是否发送完成,完成则删除 in.remove(); } return 1; } } else if (msg instanceof FileRegion) { FileRegion region = (FileRegion) msg; if (region.transferred() >= region.count()) { in.remove(); return 0; } //进行消息发送 long localFlushedAmount = doWriteFileRegion(region); if (localFlushedAmount > 0) { in.progress(localFlushedAmount); if (region.transferred() >= region.count()) { in.remove(); } return 1; } } else { throw new Error(); } // 写满了,无法再写了 return WRITE_STATUS_SNDBUF_FULL;//Integer.MAX_VALUE;}protected final void incompleteWrite(boolean setOpWrite) { if (setOpWrite) { // 还没彻底完成写操作,设置写操作 setOpWrite(); } else { // 清除写操作位 clearOpWrite(); // 刷新计划,以便处理其他任务 eventLoop().execute(flushTask); }} 6. AbstractNioMessageChannel源码分析
6.1 该类无成员变量,主要实现方法只有一个:doWrite(..)
同样的,先获取数据,发送成功则删除,发送失败则设置半包标识,发送完了跳出循环。
protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception { final SelectionKey key = selectionKey(); final int interestOps = key.interestOps(); for (;;) { Object msg = in.current(); if (msg == null) { // Wrote all messages. if ((interestOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) { key.interestOps(interestOps & ~SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); } break; } try { boolean done = false; for (int i = config().getWriteSpinCount() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 发送消息并返回成功与否 if (doWriteMessage(msg, in)) { done = true; break; } } if (done) { // 发送成功则删除已发送部分 in.remove(); } else { // 发送失败,设置半包标识 if ((interestOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) == 0) { key.interestOps(interestOps | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); } break; } } catch (Exception e) { if (continueOnWriteError()) { in.remove(e); } else { throw e; } } }} 7. NioServerSocketChannel源码分析
7.1 成员变量 & 静态方法 & 构造方法
private static final ChannelMetadata METADATA = new ChannelMetadata(false, 16);// 用于创建Channel和Selector的工厂类private static final SelectorProvider DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER = SelectorProvider.provider();private static final InternalLogger logger = InternalLoggerFactory.getInstance(NioServerSocketChannel.class);public NioServerSocketChannel() { this(newSocket(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER));}// 打开ServerSocketChannel通道private static ServerSocketChannel newSocket(SelectorProvider provider) { try { return provider.openServerSocketChannel(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new ChannelException( "Failed to open a server socket.", e); }}// 用于配置ServerSocketChannel的TCP参数private final ServerSocketChannelConfig config; 7.2 一些方法:这些方法都是获取ServerSocketChannel,然后使用它进行操作


@Overridepublic boolean isActive() { // As java.nio.ServerSocketChannel.isBound() will continue to return true even after the channel was closed // we will also need to check if it is open. return isOpen() && javaChannel().socket().isBound();}@Overridepublic InetSocketAddress remoteAddress() { return null;}@Overrideprotected ServerSocketChannel javaChannel() { return (ServerSocketChannel) super.javaChannel();}@Overrideprotected SocketAddress localAddress0() { return SocketUtils.localSocketAddress(javaChannel().socket());}@Overrideprotected void doBind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception { if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7) { javaChannel().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog()); } else { javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog()); }}@Overrideprotected void doClose() throws Exception { javaChannel().close();} 7.3 doMessageRead(..)
ServerSocketChannel接受新的客户端连接,如果SocketChannel不为空,则创建NioSocketChannel。
protected int doReadMessages(List
8. NioSocketChannel源码分析
8.1 连接操作:doConnect(..)
TCP连接操作,共三种情况:
1. 连接成功,返回连接成功;
2. 连接失败,关闭客户端连接;
3. 连接无响应,返回未连接成功,注册连接监听操作位。
protected boolean doConnect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception { // 1. 本地Socket不为空,则绑定本地Socket if (localAddress != null) { doBind0(localAddress); } boolean success = false; try { // 2. 发起TCP连接 boolean connected = SocketUtils.connect(javaChannel(), remoteAddress); if (!connected) { // 2.1暂时未连接上,服务器无应答,不确定,注册监听操作 selectionKey().interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT); } // 2.2 连接成功 success = true; return connected; } finally { if (!success) { // 3. 连接失败,关闭客户端连接 doClose(); } }}private void doBind0(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception { if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7) { SocketUtils.bind(javaChannel(), localAddress); } else { SocketUtils.bind(javaChannel().socket(), localAddress); }} 8.2 写半包
doWrite(..)通过循环的方式发送数据:
1. 读完了,清除OP_WRITE标识,返回
2. 没读完,将数据放进ByteBuffer数组中,根据数组大小进行不同的处理:
2.1. 数组大小为0:还有一些其他的东西没写,调用AbstractNioByteChannel直接写
2.2. 数组大小为1:将ByteBuffer写进SocketChannel中,如果写成功了,动态调整下次ByteBuffer数组大小并删除已写数据;如果写失败了,说明缓冲区已满,加写半包标识
2.3. 数组大小大于1:将ByteBuffer数组写进SocketChannel中,如果写成功了,动态调整下次ByteBuffer数组大小,并删除已写数据;如果写失败了,说明缓冲区已满,加写半包标识
这里有个adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(..),该方法的作用是,通过本次写入数据和待写入数据进行动态调整ByteBuffer大小:
1. 如果待写入数据等于写入数据,也就是说全写进去了,说明我设置的ByteBuffer大小优点保守,下次可以多写点,扩大每次写入的大小限制
2. 如果待写入数据大于已写入数据,也就是说没写完,分两种情况:
2.1 如果待写入数据比较大(大于4M),并且本次写入的还没有我的一半多,那说明你每次写入的太少了,这样下去要写多少次才能完,直接扩大到我的一半,写快点
2.2 其他情况(数据并不大,或者一次性写入的挺多的),说明ByteBuffer大小正合适,不需要调整
protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception { // 1 获取SocketChannel和默认循环发送次数 SocketChannel ch = javaChannel(); int writeSpinCount = config().getWriteSpinCount(); // 2. 循环发送数据 do { if (in.isEmpty()) { // 读完了,清除写半包标识,return掉 clearOpWrite(); return; } // 每次最多写多少,用以控制ByteBuffer大小 int maxBytesPerGatheringWrite = ((NioSocketChannelConfig) config).getMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(); // in.nioBuffers(ByteBuffer数组最大容量, 每个ByteBuffer最大Max字节) ByteBuffer[] nioBuffers = in.nioBuffers(1024, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite); // 获取要发送的ByteBuffer数组个数nioBufferCnt int nioBufferCnt = in.nioBufferCount(); switch (nioBufferCnt) { case 0: // 还有其他的东西待写,调用AbstractNioByteChannel进行写操作 writeSpinCount -= doWrite0(in); break; case 1: { // 只有一个ByteBuffer,直接写 ByteBuffer buffer = nioBuffers[0]; int attemptedBytes = buffer.remaining(); final int localWrittenBytes = ch.write(buffer); if (localWrittenBytes <= 0) { //缓冲区已满 incompleteWrite(true); return; } // 动态调整下次的ByteBuffer容量, adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(attemptedBytes, localWrittenBytes, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite); in.removeBytes(localWrittenBytes); --writeSpinCount; break; } default: { // 需要发送的总字节数 long attemptedBytes = in.nioBufferSize(); // ch.write(需要发送的ByteBuffer数组, 数组偏移量, 要发送的个数),返回写入SocketChannel字节数 final long localWrittenBytes = ch.write(nioBuffers, 0, nioBufferCnt); if (localWrittenBytes <= 0) { //缓冲区已满 incompleteWrite(true); return; } // 根据本次写入情况动态调整下次写入数量 adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite((int) attemptedBytes, (int) localWrittenBytes, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite); in.removeBytes(localWrittenBytes); --writeSpinCount; break; } } } while (writeSpinCount > 0); incompleteWrite(writeSpinCount < 0);}// 动态调整每次发送数据的大小private void adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(int attempted, int written, int oldMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite) { if (attempted == written) { // 数据全写进去了,说明缓冲区还挺大,一次性可以多写点,扩大一次性写入限制 if (attempted << 1 > oldMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite) { ((NioSocketChannelConfig) config).setMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(attempted << 1); } } else if (attempted > MAX_BYTES_PER_GATHERING_WRITE_ATTEMPTED_LOW_THRESHOLD && written < attempted >>> 1) { // MAX_BYTES_PER_GATHERING_WRITE_ATTEMPTED_LOW_THRESHOLD = 4096 // 本次写的少,数据又比较大,直接把最大限制设置为待写入数据的一半大 ((NioSocketChannelConfig) config).setMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(attempted >>> 1); }}